Given the negative sentiments surrounding the markets recently, the cryptocurrency industry has been facing significant headwinds. Yet, while this may call for caution, it is not the time to be bearish on crypto. Instead, times like these are opportunities to scoop up gems at a discounted price.
One such gem that I would like to introduce is Elrond, and the network’s native token is Elrond Gold (EGLD). This article serves as a brief, technical overview of the Elrond blockchain.
What is Elrond?
Elrond touts itself as an easy-to-use blockchain platform that is highly scalable, fast, and secure. Ultimately, its aim is to “onboard the next billion people, toward a multi-trillion-dollar market”.

To do so, Elrond embodies these 3 main features:
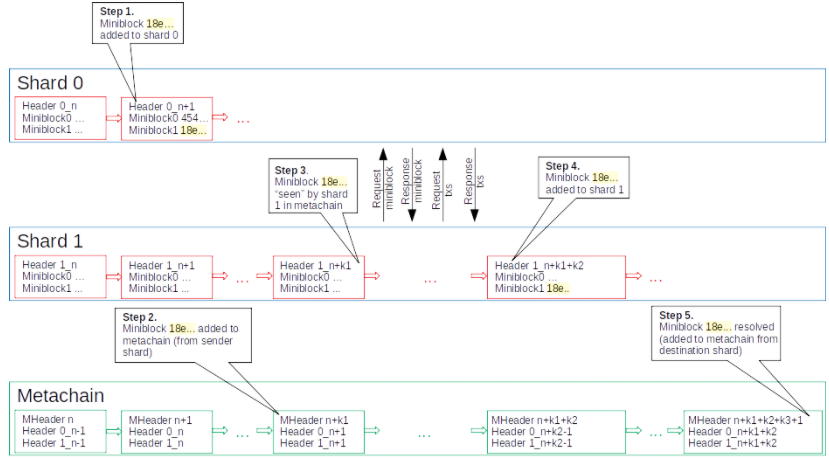
1. Adaptive State Sharding
This feature renders the platform highly scalable and fast to “onboard the next billion people” through parallel transaction processing. To unpack this, we need to understand what sharding is.
What is sharding?
Sharding is a partitioning technique for blockchains to improve their scalability. The gist of this idea is for each node of the network to process only a fraction of transactions. This allows for parallel processing of transactions, thereby improving throughput and efficiency.
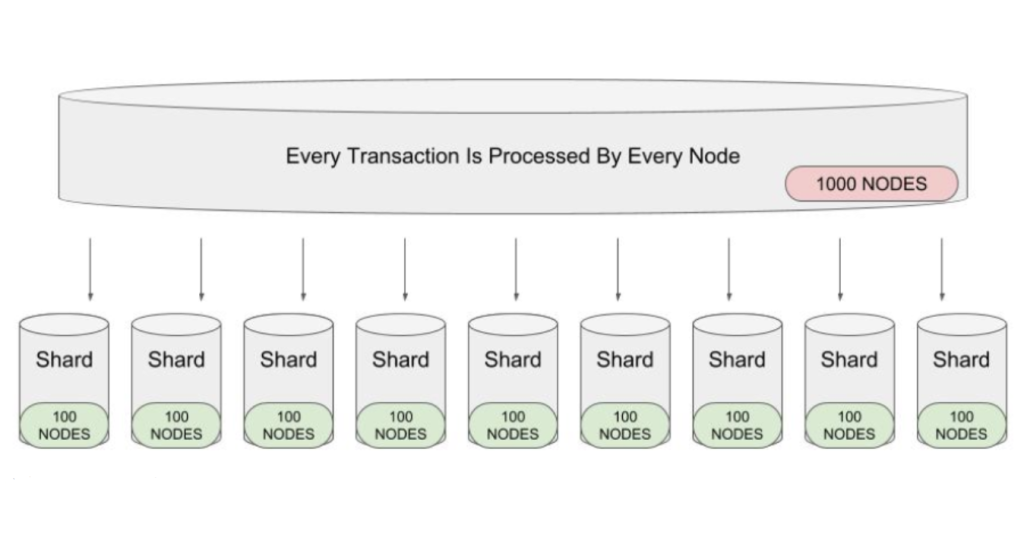
There are three different types of sharding, namely network sharding, transaction sharding, and state sharding. Essentially, Elrond is the first blockchain platform to implement all three types of sharding.
How is sharding adaptive?
Elrond also implemented an additional coordination shard AKA the Metachain. Unlike other shards that are responsible for state and transaction processing, the Metachain facilitates communications between shards.
The Metachain will control the real-time splitting and merging of shards as the demand for network capacity changes. This makes the network capacity highly malleable as user demand requires.
For instance, consider a blockchain subjected to a sudden spike in demand within the network. In this case, Elrond can adapt and scale by adding an additional shard to meet the required throughput.
As a result, Elrond’s adaptive state sharding architecture is able to handle up to a massive 263,000 transactions per second.
2. Secure Proof of Stake
This feature deals with the security of the platform to make it more attractive for businesses. This is especially crucial if businesses wish to implement Elrond’s network as part of their mission-critical operations. To understand how Elrond secures its platform, a thorough examination of the consensus mechanism employed is required.
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
Most blockchain platforms either implement a Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. Elrond and most other L1s are running on PoS, whereby the eligibility for validator selection depends on one’s stake. Conversely, both Bitcoin and Ethereum utilize a PoW approach, although Ethereum is migrating to a PoS approach for Ethereum 2.0.
Notably, this is because PoS eliminates the computational waste brought about by the PoW approach.

Security from PoS
The PoS approach implemented by Elrond somewhat safeguards the network’s security. This is because a malevolent validator needs to be selected for consensus to sabotage the network.
But to increase the likelihood of being selected, it needs to have more EGLD tokens staked. Hence, the validator’s non-trivial exposure to EGLD’s price serves as a financial disincentive that discourages them from acting maliciously.
Security from SPoS
To further enhance the security of validator selection, Elrond proposed a novel approach called Secure PoS (SPoS). Besides selecting validator nodes based on staking, SPoS goes one step further and assigns each validator an individual rating score.
During the selection process for consensus, those with higher ratings are more likely to be selected. This promotes meritocracy among validators, encouraging their operators to keep the network running smoothly.
Security from Node Collusion
To safeguard Elrond’s integrity, the nodes within its shards are reshuffled every now and then. Basically, each shard consists of nodes and there exists an inherent risk of these nodes creating unfair coalitions.
If these nodes collude, they are able to influence the addition of new blocks on the chain, thereby compromising the blockchain’s integrity. As such, the node configuration of each shard must change regularly to combat this problem of node collusion. Elrond implements this by employing a ‘node shuffling’ approach after every epoch.
What this means is that the nodes on each shard will be reshuffled and redistributed to different shards periodically. This process is governed by the Metachain, which will select the nodes and redistribute them non-deterministically.
This layer of unpredictability implies that inter-node collusion within each shard is rather impossible, thus maintaining the integrity of the chain.

3. Elrond Virtual Machine
This feature aims to enhance the ease of use of Elrond’s blockchain. This is salient because developers will only integrate their decentralized applications (dApps) with Elrond’s network if Elrond is developer-friendly.
For these dApps to function effectively, the execution of smart contracts is a priority. In providing a simple, virtual environment to support this core function, Elrond has built a virtual machine AKA Arwen.
Portability
Arwen is a dedicated smart contract execution engine built on WebAssembly (WASM). This means that smart contracts can be written in any programming language that can be compiled into WASM. These include Rust, C/C++, C#, and Typescript.
Elrond has also created the Elrond Integrated Development Environment (Elrond IDE). Coupled with its own Rust framework, this allows developers to code their smart contracts in Rust efficiently and cleanly.
However, it should be noted that Solidity (Ethereum VM’s smart contract programming language) cannot be compiled to WASM yet.
This implies that Ethereum smart contracts cannot be migrated to the Elrond Network until a Solidity-WASM compiler is developed.
API’s ease-of-use
On top of its portability, Arwen also provides an Application Programming Interface (API) called the Elrond Environment Interface. This API offers developers convenience, especially when handling calls between smart contracts.
To illustrate this, consider a smart contract on one shard calling another smart contract stored by a different shard. Without the API, the developer has to take these different shards into account when handling the execution of these calls.
But with Arwen’s asynchronous API, the execution will simply be switched to an asynchronous mode automagically. The call will then be sent to the destination shard where it will be executed before returning to the caller. This asynchronous mode is transparent to the smart contract developer since it is purely handled by the API. As a result, the developer never has to care about the different shards in Elrond’s chain.
Therefore, Arwen’s API boosts its ease of use and developer-friendliness as opposed to other sharded chains.
Wrapping Up
A quick TLDR on the above points:
- Adaptive state sharding allows Elrond to scale and handle large volumes of transactions. This benefits users of Elrond’s platform as they enjoy fast transaction speeds together with low transaction costs.
- Secure Proof of Stake consensus mechanism provides Elrond’s network with multiple layers of security. This benefits businesses as it provides a peace of mind when integrating with Elrond’s network.
- Arwen’s portability and API provides developers with an easy-to-use interface for them to write their smart contracts. This will ultimately promote native development and migration of dApps onto Elrond.
By effectively meeting the demands of stakeholders (users, businesses, developers), I believe Elrond has a chance in attaining widespread adoption. This will subsequently allow Elrond to achieve its aim of “onboarding the next billion people toward a multi-trillion-dollar market”.
Now that the technicalities out of the way, my next article will focus on Elrond’s business model.
Stay tuned!
Featured Image Credit: Cryptoast
Also Read: Introducing Defi 2.0: Exploring The Hype Behind The New Wave of Decentralised Finance