In May, OpenSea, the most popular NFT marketplace, launched SeaPort, which is an open source marketplace protocol for NFTs. So what exactly is SeaPort and what are the impacts of OpenSea’s latest move in the market? Let’s find out.
But firstly, if you would like an introduction to NFTs and OpenSea, click on the following:
Also Read: Your Complete Guide To The Largest NFT Marketplace: OpenSea
What Is SeaPort?
SeaPort is an open source protocol where anyone can now operate as an NFT marketplace.
So how is this different from the OpenSea NFT marketplace? Firstly, OpenSea is centralized and any changes to the platform are controlled by one party, namely the OpenSea company.
As Seaport is open source code, anyone can essentially use the code and build a NFT trading platform on their own. This allows for forks that can be built and encourage more adoption of the NFT space.
But other than just concerns over decentralization, what makes SeaPort unique? Well, the following might interest NFT enthusiasts.
1. Trade NFTs for Other NFTs
Currently, NFT trading on OpenSea occurs between NFTs and fungible tokens. For example, you can sell an NFT for ETH, USDC, or DAI.
In SeaPort, users can trade NFTs for other NFTs, or sell them for ETH and other ERC-20 tokens. This change also supports ERC-721 or ERC-1155 format as well.
For example, a user could “offer” a group of NFTs and a mix of ERC-20 tokens in order to exchange for 1 other NFT.
Imagine a situation where you can list your MAYC for 25 ETH, or 5 ETH + 1 Azuki, or exchange it for 2 Azukis. Or, you could even sell your EnRats for any ERC-20 token, not limited to just ETH or USDC.
This unlocks a lot more liquidity for NFTs and is essentially in my opinion, similar to how AMMs allowed for seamless trading between different tokens compared to centralized exchanges.
2. Setting Requirements
SeaPort users can now specify certain requirements on NFT pieces when making their offers. For example, a user can request to trade their NFTs for a BAYC, if and only if the BAYC has a specific trait (e.g. bunny ears).
3. Other Benefits
With SeaPort, users can launch a Dutch auction for their NFTs. A Dutch auction is when the seller first sets a maximum price. The price is gradually reduced till one buyer is found. The process continues until the supply of NFTs are all bidded for, and the price paid will be the lowest and the same for all buyers.
Another advantage is that SeaPort’s contract is also gas-optimized, which allows for cheaper transactions. That is a positive sign given that OpenSea is one of the largest gas consumers on ETH.
Lastly, OpenSea is also offering a bug bounty of up to 1 million USDC to tackle potential exploits and to improve the safety for users.
Why The Pivot?
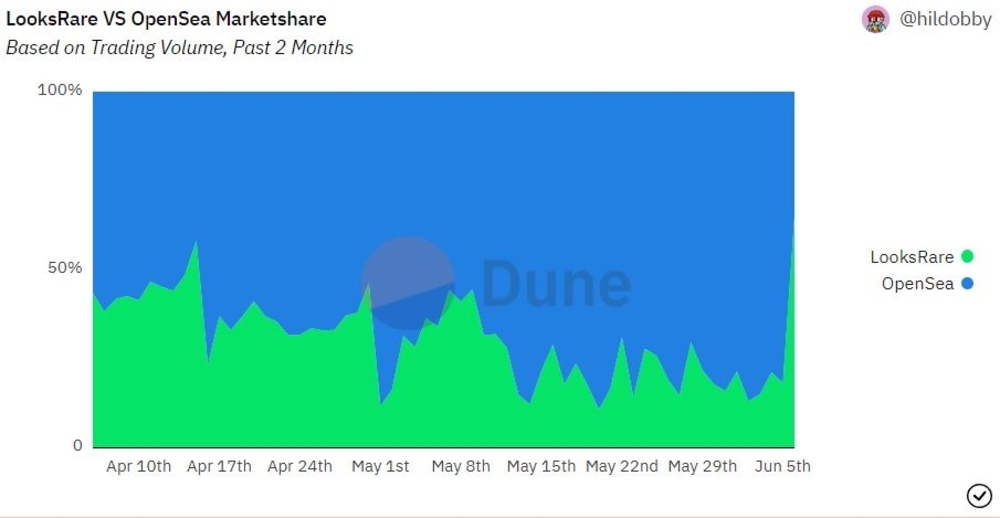
The initial market dominance of OpenSea, a centralized platform for NFT trading has led to some criticisms of OpenSea and NFT trading as a whole.
The beauty of Web 3.0 and the market of course dictated a necessary change. In January, a “vampire attack” that aimed to draw NFT trading volume away was conducted on OpenSea.

In January 10, the competitor LooksRare was officially launched by 2 anonymous founders, with a token LOOKS that was airdropped to OpenSea users. The LOOKS token also allowed for revenue to be given back to stakers.
This new token model and buzz around a new competitor quickly allowed LooksRare to propel into success, rivalling OpenSea in total NFT volume traded.
There are also existing competitors which provide similar functions to SeaPort. For example, Sudoswap is currently an AMM that allows for NFT trading. These other platforms highlight how competitive the NFT industry actually is, and the need for OpenSea to constantly innovate and attract users.
Closing Thoughts
Given that the NFT marketplace is largely competitive with different teams targeting pain points for users, I find it unsurprising that OpenSea has made has made a move towards being more decentralized and Web 3.0 focused.
OpenSea may have the advantage of being the most popular NFT marketplace with a large team. Furthermore, the long term vision of the OpenSea team when it comes to SeaPort is something to look out for as well.
A technical deep dive for developers and conversation with the OpenSea’s Head of Protocol Development can be found here:
Here is my conversation with @z0age
— Sina (@sinahab) June 2, 2022
We dive into Seaport, the new marketplace protocol developed by @opensea — talking about how the protocol is architected; how conduits and zones work; we even get into some of the low level gas optimizations in the contracts pic.twitter.com/xbWMDtuuLh
“One other big benefit of if we can all work together to build a really rock solid primitive, that is flexible enough for all these different use cases, then there’s nothing stopping us from deploying it across every EVM compatible too” – 0age, OpenSea’s Head of Protocol Development
The launch of SeaPort could allow the NFT market to blossom and onboard even more users.
It is worth noting that since this is an open source protocol and not a specific platform run by OpenSea, it might not seem beneficial for them as they do not take any fees and any developer can create a competitive marketplace with SeaPort.
Perhaps OpenSea wants to catalyze and kickstart innovation. This could be the key for greater adoption and more enthusiasm for NFTs, allowing the entire market to grow and scale to users demand.
Either way, the NFT marketplace space is brimmed with competition – may the best development and competitor win.
[Editor’s Note: This article does not represent financial advice. Please do your own research before investing.]
Featured Image Credit: Chain Debrief
Also Read: Your Complete Guide To The Largest NFT Marketplace: OpenSea