The aptly termed “flash loans” allow users to borrow and repay a loan almost instantly. So, what are flash loans, why do we need them, and are they good or evil for Web3?
If you are an avid user of DeFi, you likely know that most loans require over-collateralization. Due to the lack of credit scores and KYC, protocols manage risk by requiring users to deposit more than the borrowed amount.
While there are innovations in the works to eventually overcome this, there is one form of loan requires no collateral.
What Are Flash Loans
Flash Loans are a method to borrow a large number of tokens and repay them, with no collateral posted. The catch is that both must be done in a single transaction (one block for Ethereum), with a set lending fee.
If even one part fails, the whole sequence fails and the flash loan will not be processed.
So, why would anyone do this?
The funds can be used between borrowing and repayment. This leaves room for leveraged profits, where users can take advantage of tiny opportunities with huge amounts of capital.
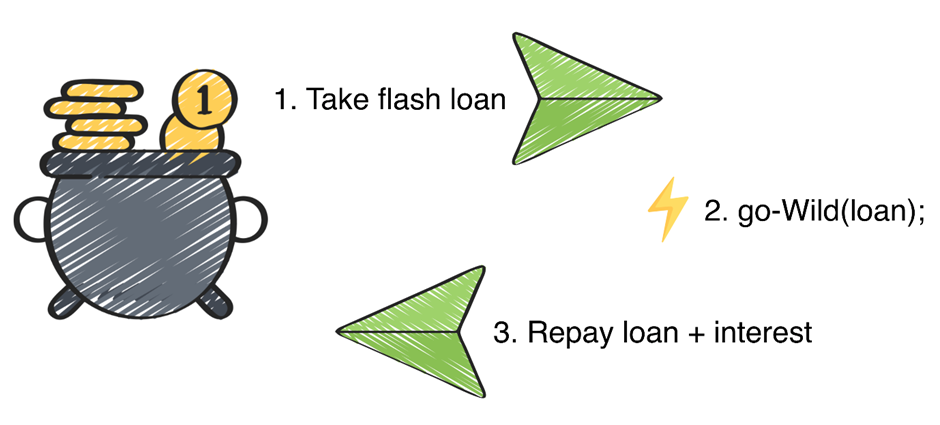
Step 1:
The loan transaction is submitted to the chain, which then lends funds to the borrower.
Step 2:
The borrower can do anything with the funds.
Step 3:
The borrower pays back the funds in time, and the transaction ends.
If the borrower does not pay back the loan before the transaction ends, repayment is enforced by the smart contract, like the loan has never happened in the first place.
This leaves us with three main use cases for flash loans, namely:
- Arbitrage
- Swapping Collateral
- Self-Liquidation
Currently, Aave is the largest provider of such services, with more than $9 Billion in flash loans taken to date.
Using Flash Loans for Arbitrage
Possibly the simplest out of the three, flash loans can exponentially increase a user’s gain.
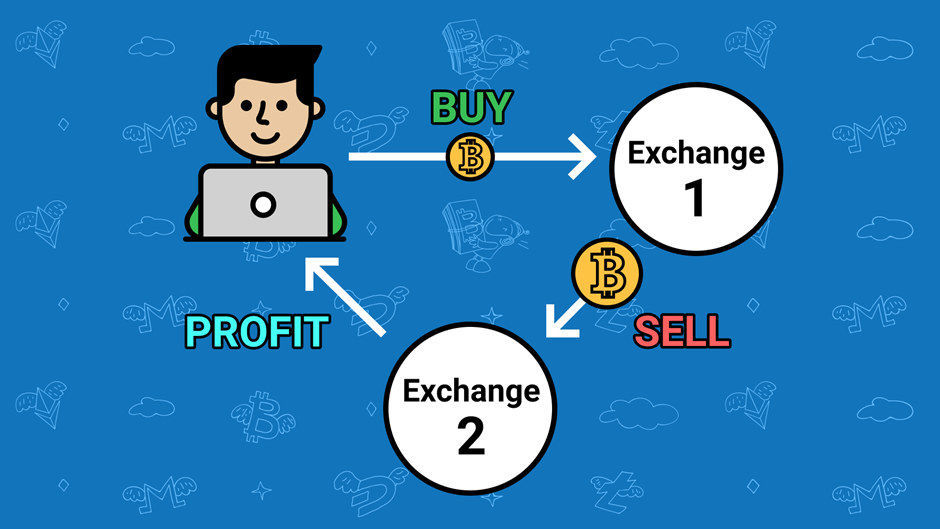
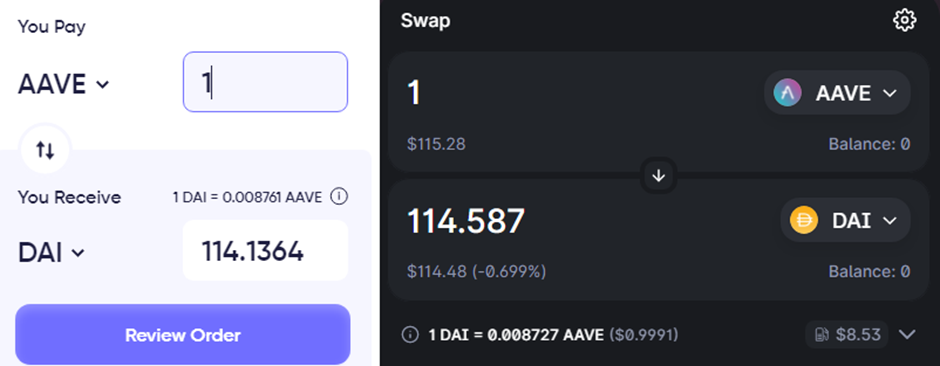
For example, AAVE/DAI is currently trading for $114.1365 on Matchswap, and $114.587 on Uniswap. Buying 1 $AAVE on matchaswap and selling it on Uniswap therefore nets a profit of $0.4506.
By using a flash loan, you can perform this transaction with $1 million without having any collateral. After fees, this should leave you with roughly $3000 in pure profits.
This is therefore a net good for most protocols, as it helps to keep prices in check without any additional work. However, low liquidity and high slippage on altcoins usually reduce profits significantly, and therefore does not present many arbitrage opportunities.
Swapping Collateral
A more unique method of using flash loans is swapping the collateral in a vault. Due to crypto markets being volatile, you may lose trust in the form of collateral in a vault and wish to change it to something more stable.
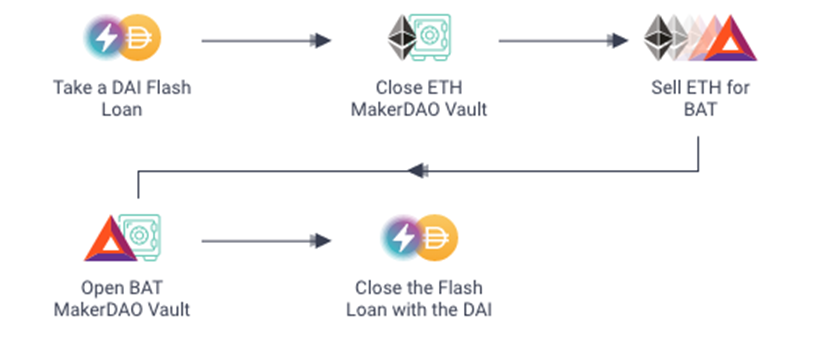
To do this, the flash loan creates a series of transactions where:
- A flash Loan is taken
- Loan is used to repay debt and withdraw collateral
- Swap old collateral with new collateral
- Use new collateral to take out the same loan
- Repay the flash loan
This is especially useful for those who do not have sufficient capital to perform the swap, or just want a quick method. This also protects them against slippage, as the transaction can simply fail if step 3 occurs at a bad price.
Swapping collateral allows users to protect against liquidation risks and retain borrowing power in choppy markets.
In a time where alts are falling immensely against $BTC and $ETH, flash loans are one of the many ways to prevent losing a large chunk of collateral.
Self-Liquidation
While it may seem counter-intuitive to liquidate your position, it can save users a lot of money.
A good example is when $LUNA’s price kept falling, and many users lacked the funds to repay their debt. Instead of letting Anchor Protocol liquidate your collateral, you could use a flash loan to protect some of it.
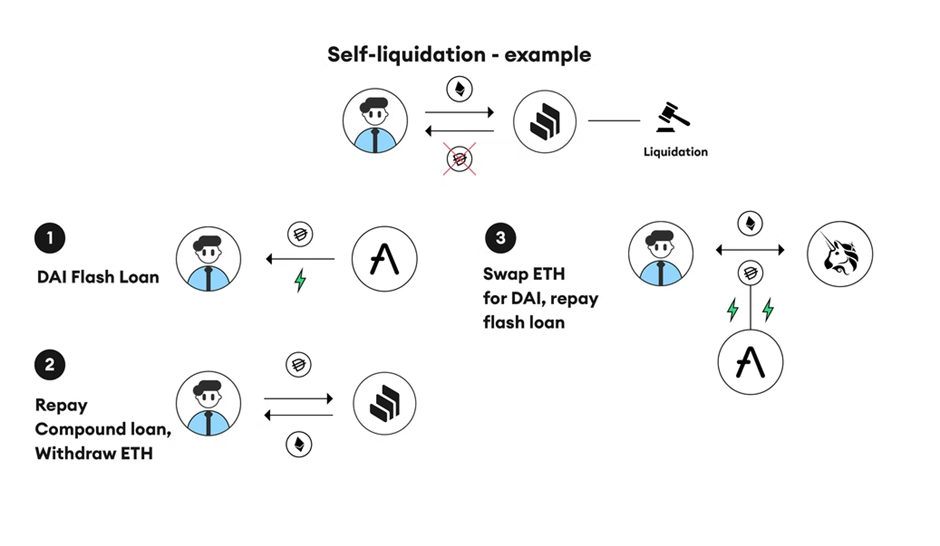
The Flash Loan processes a series of transactions where:
- A flash loan is taken for the amount owed
- Repay the initial loan to redeem the collateral
- Swap Collateral to repay flash loans and fees
By doing so, you can retain the remaining collateral, while avoiding typically high liquidation fees. Instead of paying roughly 5%-15% fees, you only pay network and borrow fees.
Flash loan attacks
Cheesebank and Uniswap
While the aforementioned methods of using flash loans are mostly a net good, they are often portrayed negatively in the media. Though they help reduce inefficiencies in the market, they can also be used to heavily exploit small errors.
This is getting absolutely ridiculous, it's the FOURTH flash loan funded price oracle attack in the past month alone
— ChainLinkGod.eth (@ChainLinkGod) November 16, 2020
I can't be any more clear, price oracles that fetch market data from only a single exchange is vulnerable to market manipulationhttps://t.co/e6Xk6a63y4
This can be done easily on protocols that use a singular or centralized price oracle, such as a Decentralized Exchange. By taking a flash loan, they can push the price of a token up or down temporarily and use that to siphon funds.
Mirror Protocol
Mirror Protocol is being exploited again as we speak, and the devs are completely MIA. So far, the attacker has drained over $2m and counting – the attack will get worse when markets open tomorrow unless the dev team steps in and fixes the price oracle. @mirror_protocol (1/4)
— FatMan (@FatManTerra) May 30, 2022
Terra’s collapse has led to a multitude of protocols also being exploited, as they hardcoded $UST to $1 or simply cannot process how low Luna Classic is trading for.
Flash loan attack on bZx
Two high-profile flash loan attacks saw attackers run off with almost $1,000,000 in value at the time. Both attacks followed a similar pattern on bZx.
Attackers spontaneously borrowed hundreds of thousands worth of ETH, funnel it through a chain of vulnerable on-chain protocols and extracted hundreds of thousands of dollars in stolen assets. They thereafter, paid back their massive ETH loans.
The attacker took out an ether flash loan on dYdX, then divided that loan and sent it to two other lending platforms: Fulcrum and Compound.
On Fulcrum, a bZx protocol, the attacker used part of the loan to short ETH against WBTC, which means the platform now needed to acquire WBTC.
This information was passed to Kyber, another DeFi protocol which filled the order on Uniswap. Yet, this resulted in low liquidity on Uniswap and the price of WBTC surged immediately, meaning that Fulcrum overpaid for the WBTC.
At the same moment, the attacker used the rest of the loan to borrow WBTC from another DeFi protocol named Compound. After reselling the borrowed WBTC on Uniswap to get a decent profit, the attackers repaid their loan and pocketed the remaining ETH.
Closing Thoughts
Flash loans can help bridge many of the inefficiencies in DeFi while making users a heavy profit along the way. Exploits are also often the result of projects not undergoing proper security audits.
Furthermore, while performing a flash loan may seem complicated, sites like furucombo are making it increasingly accessible for even retail users.
It is also important to note that flash loans represent the early stages of DeFi. As use cases and the technology itself develops, we may one day see undercollateralized, decentralized lending – all available on the blockchain.
[Editor’s Note: This article does not represent financial advice. Please do your own research before investing.]
Featured Image Credit: Chain Debrief