When valuing a cryptocurrency or blockchain protocol, one common metric that often pops up is the market cap and the fully diluted market cap.
While both may be somewhat similar in value, they represent two different meanings. Here’s a look at the difference between the market cap and the fully diluted market cap of a cryptocurrency and why it matters.
Market cap in crypto
Market capitalization (market cap) is the total network value of the crypto at any one point of time, or the sum of all the coins currently in circulation multiplied by the current price of the coin.
Circulating supply of coins x Price per coin = Total crypto market capitalization
Market cap is often used to rank the popularity and size of the cryptocurrency — a cryptocurrency with a higher market cap is often regarded as more popular, as there are more crypto holders willing to hold the coin at the current price, contributing to a higher network value.
A cryptocurrency with a higher market cap is also more likely to be a more stable investment than another one with a much smaller market cap as the smaller market cap cryptocurrency is more susceptible to price movements.
A fully diluted market cap
A fully diluted market cap on the other hand, measures the market cap when all of the coins are issued. It is the sum of the maximum supply of the coin multiplied by the current price of the coin.
Maximum supply of a token x Current market price of the token = Fully diluted market capitalization
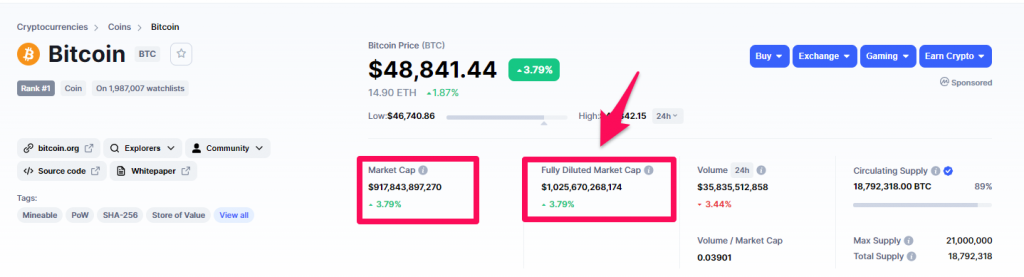
For example, the amount of Bitcoin in circulation is currently 18.782 million, while the total amount of Bitcoin that will ever be minted is 21 million.
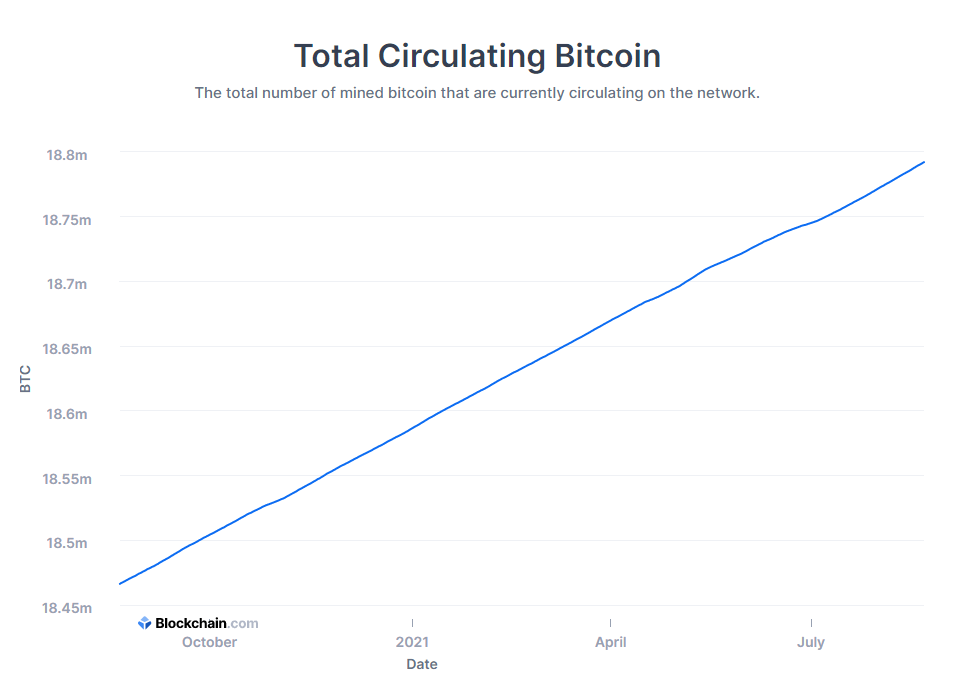
Hence the market cap and fully diluted market cap of bitcoin is:
| Bitcoin | Metric |
| Current Price (a) | $48841.44 |
| Total Supply (b) | 21,000,000 |
| Current Supply (c) | 18,792,000 |
| Market Cap (a x c) | $917.8 billion |
| Fully Diluted Market Cap (b x c) | $1.025 trillion |
The implications of a fully diluted market cap
The problem with the fully diluted market cap is that while it shows a higher market cap, it ignores any potential decrease in price of the token with the eventual increase in its circulating supply.
Fully diluted market cap assumes that the market cap in the future will increase in direct proportion to the current circulating supply at any given time.
However, that may not be the case. In theory, the supply of the token increases, it should push down the price of the token due to oversupply, causing token inflation.
Hence when investors look at fully diluted market cap, they should be mindful that the metric does not take into account the impact of inflation towards the fully diluted market cap.
Should investors care about fully diluted market cap?
With these concerns, should investors then look only at the current market cap of a cryptocurrency and not care about its fully diluted market cap?
The fully diluted market cap can be used as an indicator of the impact of future supply into the market. In the cryptocurrency space, many people are afraid of the increasing supply of coins or tokens.
The fully diluted value market cap may be a good metric for long-term investors, as it allows them to better judge whether a project’s value is reasonable. An extremely high fully diluted market cap means that there will be a lot more tokens that will come into circulation.
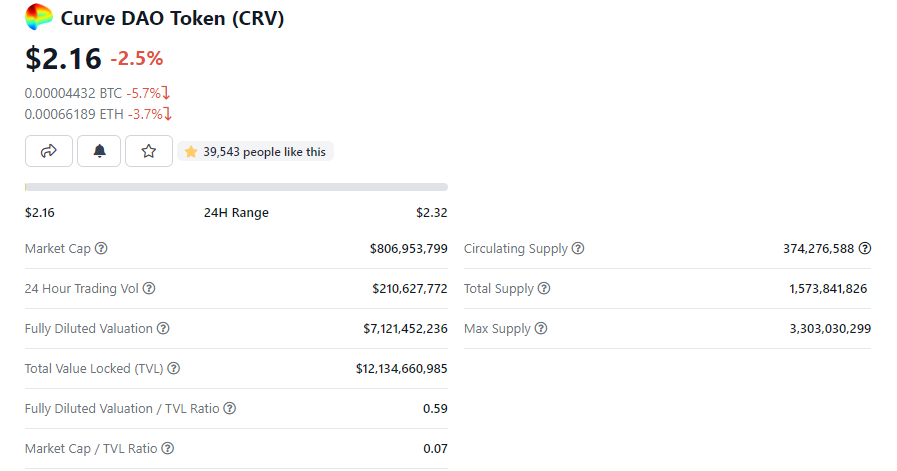
Preferably, the market cap and its fully diluted market cap should be similar in value.
A higher than normal fully diluted market cap means that there is a large amount of supply of the token scheduled to be released to the market, thereby providing a high selling or inflationary pressure to the token. It is preferable for tokens to have a hard cap or locked tokens to ensure that there are no sudden huge inflationary pressure from an influx of new coins.
Some other factors to consider:
- What is the schedule for release of future coins? Will the circulation double in the next year or is it set to release a fraction of a percentage every year for the next hundred years?
- How useful is the token, and what type of growth is expected?
- How is the circulation impacted by its staking rewards?
Another common mistake that investors may make is assuming that the value of the company is similar to the market cap of the token.
It is important to differentiate that the market cap measures the token’s network value, not the value of the company. The token may survive over time as long as there are user, but the company may not.
Take Binance and its native token BNB for example — Binance might cease to exist next year, but BNB’s DEX and Binance Smart Chain can run forever as long as there are nodes running and developers maintaining the network.
If you are looking to sign up for a crypto exchange, check out FTX. FTX also has a referral program, and you can get 5% off your trading fee with this referral code. https://ftx.com/#a=36327662
Featured Image Credit: CNBC
Also Read: New To Crypto? Here’s How To Start Investing In Cryptocurrencies In Singapore