Behind every successful project, there is solid tokenomics. Tokenomics is the foundation of every project and it would make or break the project depending on how it is structured.
Newbies often get rekt as they don’t understand the tokenomics behind the project and how to differentiate the good from the bad.
I too, have been burned by projects with bad tokenomics because I didn’t understand the fundamental of tokenomics.
What is Tokenomics?
Before we dive into five things you need to know about tokenomics, we first need to know what tokenomics is.
Tokenomics is a combination of token and economics. It refers to the economic properties that a token possesses and it encompasses a range of qualities such as emission rate, token supply, vesting schedule and many more.
Tokenomics is by far one of the most difficult things to grasp when reviewing a project. It is often discussed but rarely understood.
Projects with well-designed tokenomics are much more likely to succeed in the long run whereas projects with poor tokenomics are bound to fail.
Token supply
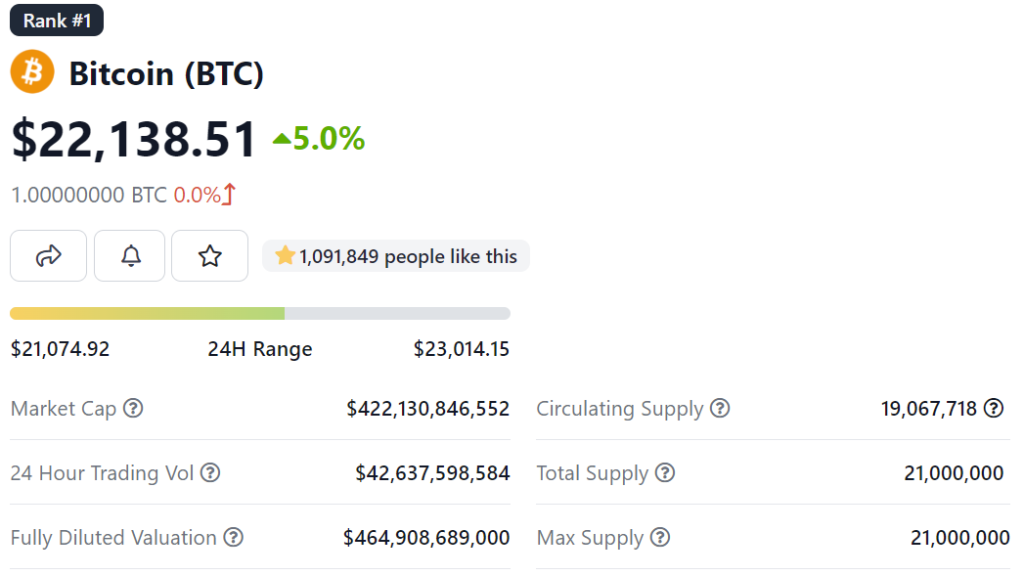
Token supply is very important as it directly impacts the perceived value of the token. Depending on how scarce the tokens are, the perceived value might increase or decrease.
By default, perceived value is inversely correlated to token supply. When the token supply is low it is automatically deemed valuable, and vice versa. However, scarcity is only one of the few factors that affect the perceived value as the token is not automatically valuable because it is scarce.
There are four key supply metrics to look out for:
- Circulating supply
- Maximum supply
- Market cap
- Fully diluted market cap
Circulating supply or current supply refers to the number of tokens that are currently in circulation that are available for investors to trade.
Maximum supply refers to the maximum amount of tokens that would be available in the market. Most governance tokens would have a max cap but some tokens are inflationary and do not have a max cap.
Market cap is the circulating supply multiple by the current price. It is a way to measure the token value and its capacity to grow. For instance, tokens with a smaller market cap have more capacity to grow compared to tokens with a large market high.
Fully diluted market cap is the maximum supply multiple by the current price. It is a way to measure the token value when all the tokens have been mined or unlocked.
These few metrics would help to paint a better picture of how the token price would change in the future. For example, if the circulating supply of token A is at 30%, when the rest of the token is unlocked it would put pressure on the token price.
Inflationary and deflationary tactics
Cryptocurrency inflation is technically the same as fiat inflation. Inflation occurs when the number of tokens in circulation is on the rise and vice versa for deflation.
Inflation is a silent killer as tokens are slowly distributed which increases the circulating supply and the token gradually becomes worthless.
Most projects would constantly rely on token emissions to reward investors. The price of PancakeSwap has been on a downward trend because it is constantly relying on token emission to sustain the high APYs.
🔥 🔥 🔥 🔥 🔥 🔥 🔥 🔥 🔥 🔥 1,830,382 #BNB (772,363,806 USD) burned at #Binancehttps://t.co/x1VxRpqgt1
— Whale Alert (@whale_alert) April 19, 2022
To counter inflation, some projects would introduce deflationary mechanisms to keep inflation in check. One notable example is the recent quarterly BNB burn. A total of 1.8 Million BNB valued at US$772 Million was burned by Binance.
This quarterly burning event helps Binance to retain value on its native token. Burning the token would reduce the circulating supply and inherently increases the price of the token.
Allocation and distribution
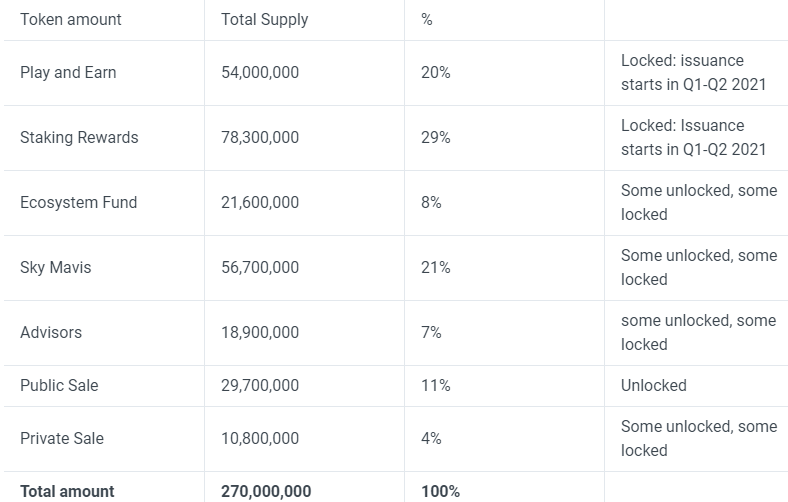
Always look into the token distribution and allocation. Knowing how many tokens each party hold could potentially help smart investors avoid the big price crash.
Some Venture Capitalists (VCs) and whales in the crypto space are notorious for dumping tokens for a quick payday.
But then again not all of them are here for quick cash as some are trying to revolutionise the space. From time to time, both the project team and VCs would need to sell tokens to raise capital for expenditure.
Knowing how many tokens they have can help you prepare for the potential price crash as the selling of tokens would inevitably lead to downward pressure on prices.
Vesting schedule
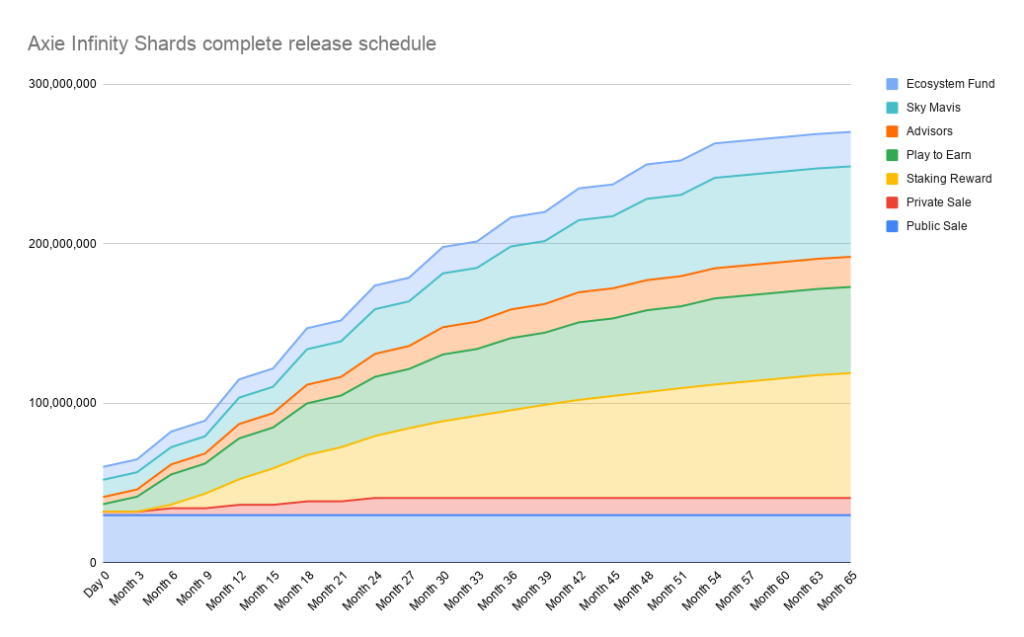
This brings us to the next point is there a vesting schedule? When is the token unlocked and how much of it will be unlocked?
Vesting period refers to the period of time the token is lockup and it cannot be sold by the investor or team. Most projects would have a vesting period and it could last anyway from 0 to 48 months.
A longer vesting period would signal team/VC confidence in the project and generally, it would do better than a project with a shorter vesting period.
The main reason for vesting is to prevent the team or VC from dumping the token once it goes up on the market.
Knowing and actively tracking the vesting schedule could help investors get ahead of the game. This could help the average investor avoid the massive price crash caused by dumping from either the team or the VCs.
Token utility
How do you keep the token price from falling? The answer is utility. Token utility is one of the many few mechanisms able to generate demand for the token. Generating demand helps to lower or stop the selling pressure of the token.
Token utility can come in many forms. One way blockchain introduces token utility to the native token is by making it the currency of the network. Users who want to make a transaction on the network would need to pay a transaction fee (gas) using the native token.
The Ethereum blockchain is a very good example. Every transaction on the Ethereum network requires users to pay a gas fee. This creates a demand for ETH as users who wants to use the network needs to have ETH in their wallet.
Not sure what is gas fees are used for?
Also Read: What Are Gas Fees? Why They Get So High On Ethereum, And How To Adjust It On MetaMask
Conclusion
Without a doubt, the supply and demand forces determine the token price. An increase in the supply of tokens and a drop in demand would definitely see the token price start to fall.
This is a very common scenario in the crypto space, especially those yield farming tokens. Of cause, there are some exceptional projects that are able to create demand for their token so the increasing supply of tokens is mitigated by even higher demand.
At the end of the day, these are just some basic tokenomics frameworks to look out for when evaluating projects. There are still other factors to consider but these five factors are a good starting point.
[Editor’s Note: This article does not represent financial advice. Please do your own research before investing.]
Featured Image Credit: Chain Debrief
Also Read: Crypto Will Shake Up TradeFi: 5 Reasons Why Blockchain Tech Will Disrupt The Finance Industry