A widely-anticipated upgrade to Ethereum, which is the second largest cryptocurrency in the market, was recently initiated on August 4. Called the London Hard Fork, the upgrade represents a series of improvements to the underlying technology to improve the network’s scalability and security.
The London Hard Fork consists of five sets of technical upgrades, which are aptly named Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIP). EIPs are proposals drafted by members in the community that recommend a change on the underlying codes, in a bid to improve the protocol.
The most prominent EIP in the London hard fork is the EIP-1559, which aims to make transactions on Ethereum more efficient by simplifying its fee structure and on a macro basis, changing its monetary policy.
This has seen great support from the community, especially since more than $5 million is spent on transaction fees on the Ethereum network alone. This is in stark comparison with Bitcoin, the largest cryptocurrency in the market, where the daily transaction fees stand at only $1.5 million.
Understanding the Ethereum roadmap
Before delving into the mechanics of EIP-1559 and how it will affect the network, it is essential to first understand Ethereum’s roadmap and its evolutionary path.
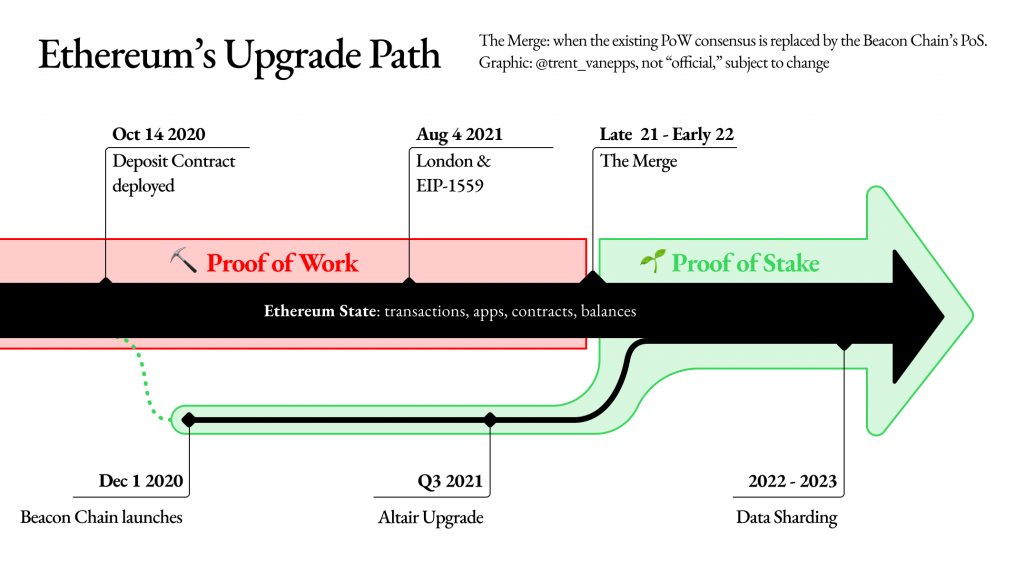
As the leading blockchain for decentralized applications (dApps), a core issue for Ethereum, and any public decentralized blockchain for that matter, is scalability. Ethereum’s popularity has resulted in network congestion that has made the cost of transactions relatively high.
Ethereum 2.0, also called Serenity, is the next evolution of the technology that will move Ethereum away from its current Proof-of-Work (POW) model to a more scalable and environmentally-friendly Proof-of-Stake model.
POW requires physical computing power (called miners) and electricity to validate transactions (grouped in blocks) in the network. POS, on the other hand, allows for participants to validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold.
Ethereum’s POS blockchain will ensure that the amount of computing resources needed to ‘mine’ transactions is tremendously reduced whilst ensuring scalability through the implementation of various innovative solutions that can process transactions at a much higher capacity.
The London hard fork is one of the last upgrades of Ethereum 1.0 that operates on a POW model, and one that brings Ethereum closer to the proposed transition towards a POS model.
What is the London Hard Fork?
The London Hard Fork is part of the Ethereum roadmap in transitioning towards Ethereum 2.0. The transition towards an Ethereum POS system has been a highly anticipated event for years, since greater transaction throughout would result in lower fees and much faster transaction times.
A hard fork refers to a permanent and foundational change to the underlying protocol, wherein the implementation of the new and proposed change will create a new fork, or a divergence, from the old blockchain.
Ethereum London Hard Fork — 5 Key EIPs#Ethereum #LondonHardFork #PocketBits♾ pic.twitter.com/DfX79ixKVL
— PocketBits (@PocketBitsIndia) August 4, 2021
The London hard fork aims to upgrade the speed of transactions as well as the incentivization of mining on the Ethereum blockchain. Ethereum is currently a cryptocurrency with an inflationary supply, which is the opposite of Bitcoin’s fixed supply. After much discussions. With the most recent upgrade, Ethereum’s monetary supply would be less inflationary and therefore, more valuable in the long run.
What is EIP 1559 and will Ether become deflationary?
EIP-1559 is a prominent proposal as it aims to introduce a new fee structure that will make Ethereum a deflationary system. On a deeper level, EIp-1559 will make transactions more efficient by utilizing a hybrid system of tips and base fees to incentivise miners more evenly.
The base fee refers to an algorithmically derived price that needs to be paid for every transaction on the Ethereum blockchain while tips refers to additional fees that users can include to speed up their transactions, especially in periods of high congestion.
Fundamentally, EIP-1559 would replace Ethereum’s current auction system of users bidding for block space through inputting their own variable gas prices, which has led to constant overpayment for gas fees.
With a newly-introduced base fee into the protocol, the transaction fees will be automatically set relative to the activity levels of the network. This will introduce predictability in transaction fees for users.
Equally important is the fact that base fees will not be kept by miners and instead will be destroyed or burnt. This will reduce Ether’s circulating supply and potentially push up the price of the coin in the long-run due to the nature of scarcity.
#EIP1559 is burning ~0.77 ETH per block over the last 48 hours. At this rate, it would burn 1.6 million ETH (worth $5 billion) or ~1.4% of the existing $ETH supply per year. pic.twitter.com/vM9EIqSBW1
— Victor "DeFi Toronto" Li ?? (@CryptoEcon_Li) August 14, 2021
Another significant EIP included in the London hard fork is EIP-3554, which introduces a steeper mining difficulty adjustment to incrementally wean the incentives for mining on the POW network. This is a vital step in preparing miners for the transition to the new POS blockchain while freezing the POW network down the line.
How Will EIP-1559 Impact Ethereum?
EIP-1559 will benefit the ecosystem, as well as the value of Ether, in a number of ways;
- Reduce transaction times and removal of fee uncertainty that has dampen user and developer experience and adoption
- Create a strong relationship between Ethereum’s native coin, Ether, with the use of dApps across the network
- Facilitate a deflationary supply mechanism to enable scarcity
All these combined would create an enhanced user experience for the most popular smart contract blockchain in the market. London hard fork is a culmination of the community’s ongoing innovation and betterment of the network to create a stronger ecosystem.
- EIP 1559 introduces a new fee structure to make Ethereum less inflationary. This protocol change is highly controversial because it aims to burn part of the fees, hence decreasing miner revenue.
- EIP 3554 delays Ethereum’s difficulty bomb to Dec. 1. This mechanism will incrementally increase the difficulty of mining on the Ethereum network, effectively “freezing” proof-of-work in preparation for Ethereum’s move to proof-of-stake.
Featured Image Credit: Currency
Read also: How To Get Started With Decentralised Finance (DeFi) For Beginners